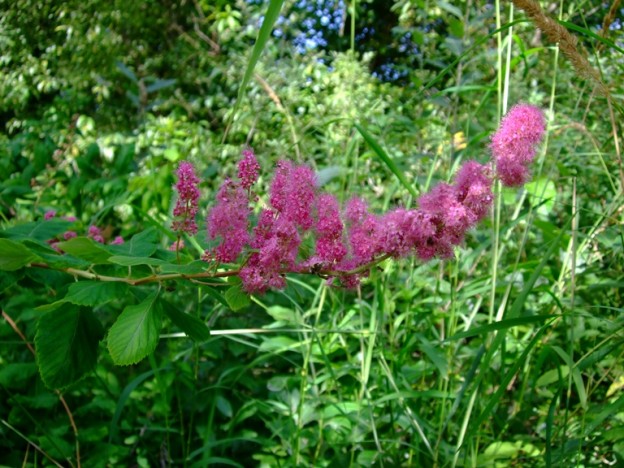
Douglas Spiraea The Rose Family–Rosaceae
Spiraea douglasii Hook.
(spy-REE-uh duh-GLASS-ee-i)
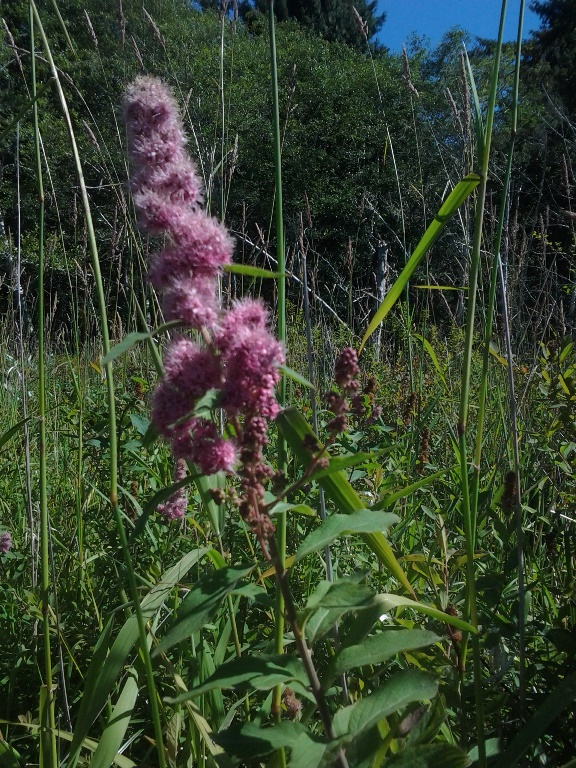 Names: The word Spiraea comes from a Greek plant that was commonly used for garlands. Douglas Spiraea is named after David Douglas. It is also commonly known as Hardhack, Steeplebush, or as Western, Pink or Rose Spiraea. There are two recognized varieties, var. douglasii, which has grayish wooly hairs on the undersides of its leaves; and var. menziesii, (sometimes known as S. menziesii) which has smooth or only slightly hairy leaves.
Names: The word Spiraea comes from a Greek plant that was commonly used for garlands. Douglas Spiraea is named after David Douglas. It is also commonly known as Hardhack, Steeplebush, or as Western, Pink or Rose Spiraea. There are two recognized varieties, var. douglasii, which has grayish wooly hairs on the undersides of its leaves; and var. menziesii, (sometimes known as S. menziesii) which has smooth or only slightly hairy leaves.
Relationships: Spiraeas are collectively known as Meadowsweets. There are about 80-100 species of spiraea in the temperate regions of the northern hemisphere-the majority in eastern Asia. Many are grown for ornamental landscaping and there are several cultivated varieties, mostly of the Japanese species.
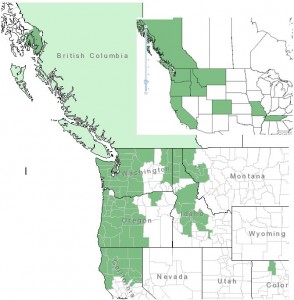
Distribution of Douglas Spiraea from USDA Plants Database
Distribution: Douglas Spiraea is native from southeast Alaska to northern California. Although it mostly occurs west of the Cascade Mountains, it is also found in eastern Washington, Idaho and western Montana. Douglas Spiraea has also been found growing in isolated counties of Colorado, Missouri, and Tennessee.
Growth: Spiraea douglasii grows 3-6 ft (1-2 m). It spreads by rhizomes, and is very aggressive, It often forms dense colonies and can quickly become the dominant species in a wetland habitat.
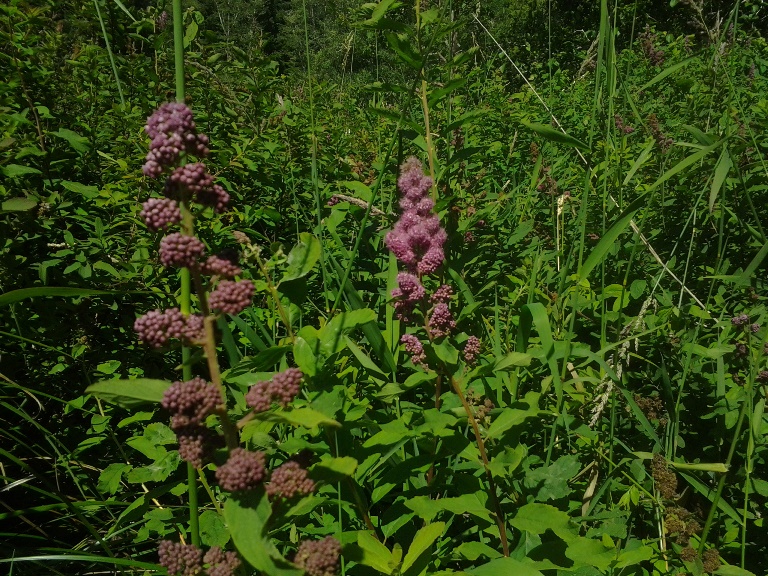
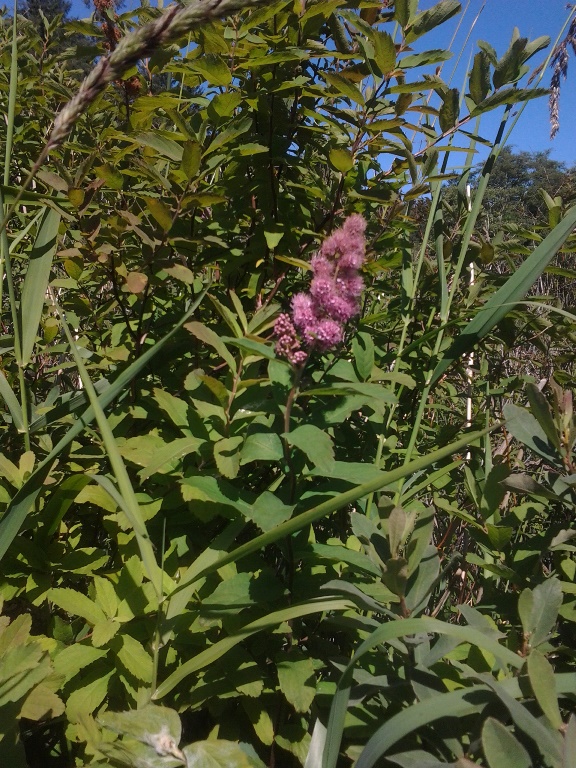
 Habitat: Douglas Spiraea grows in open areas of wet meadows, bogs, streambanks, and lake margins. Labrador Tea, Ledum groenlandicum, is often a companion of Douglas Spiraea in bogs. It can withstand drier periods in areas that are only seasonally wet. Wetland designation: FACW, It usually occurs in wetlands, but is occasionally found in non-wetlands.
Habitat: Douglas Spiraea grows in open areas of wet meadows, bogs, streambanks, and lake margins. Labrador Tea, Ledum groenlandicum, is often a companion of Douglas Spiraea in bogs. It can withstand drier periods in areas that are only seasonally wet. Wetland designation: FACW, It usually occurs in wetlands, but is occasionally found in non-wetlands.
Diagnostic Characters: This species has oblong to oval leaves that are toothed above the middle. The undersides of the leaves are paler than the upper sides and are often covered with wooly, gray hairs. The flowers are purplish-pink clustered in an upright plume or “steeple.” The fruits are pod-like follicles (dry one-celled seed capsules, which split open one side).
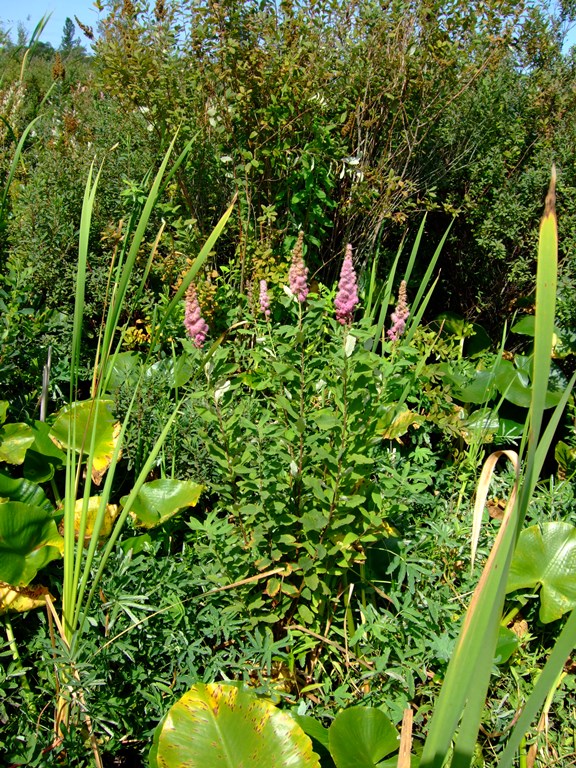 In landscapes: Douglas Spiraea is especially useful in Rain Gardens, but care should be taken not to introduce it to an area where it is likely to overtake other desirable plants. It is a good choice for revegetation projects along streamsides. Its attractive purplish-pink flower plumes create a “sea of pink” in “Hardhack bogs” when in bloom.
In landscapes: Douglas Spiraea is especially useful in Rain Gardens, but care should be taken not to introduce it to an area where it is likely to overtake other desirable plants. It is a good choice for revegetation projects along streamsides. Its attractive purplish-pink flower plumes create a “sea of pink” in “Hardhack bogs” when in bloom.
Phenology: Bloom time: July-August; Fruit ripens: September-October.
Propagation: Douglas Spiraea is easy to start from seed. Fresh seed does not require stratification; dry seed may require 1-2 months cold stratification. Douglas Spiraea may also be propagated from stem or root cuttings, or division. After a fire or burial, it readily sprouts from the stem base and rhizomes. Douglas’ spirea showed extensive rhizome and adventitious root development in tephra after the 1980 Mt. St. Helen’s volcanic eruption.
Use by people: Some natives used Douglas Spiraea for spreading and cooking salmon and for making tools to collect dentalia shells for trade and decoration. The flowers are can be dried and used in floral arrangements.
Use by Wildlife: Douglas Spiraea is sometimes browsed by Black-tailed Deer. Flowers are pollinated by insects. In bogs, it provides cover for many water birds, such as Marsh Wrens, but alternatively may provide good hunting habitat for raptors.
Links:
Consortium of Pacific Northwest Herbaria
WTU Herbarium Image Collection, Plants of Washington, Burke Museum
E-Flora BC, Electronic Atlas of the Flora of British Columbia
Jepson Eflora, University of California
Ladybird Johnson Wildflower Center
USDA Forest Service-Fire Effects Information System
Native American Ethnobotany, University of Michigan, Dearborn

